In the vast landscape of computer hardware, few components are as integral and enigmatic as the motherboard. Serving as the central hub that connects all other hardware components, the motherboard plays a pivotal role in the functionality and performance of your computer. In this article, we’ll delve into what a motherboard is, explore its different types, and examine the various components that make up this crucial piece of hardware.
What is a Motherboard?
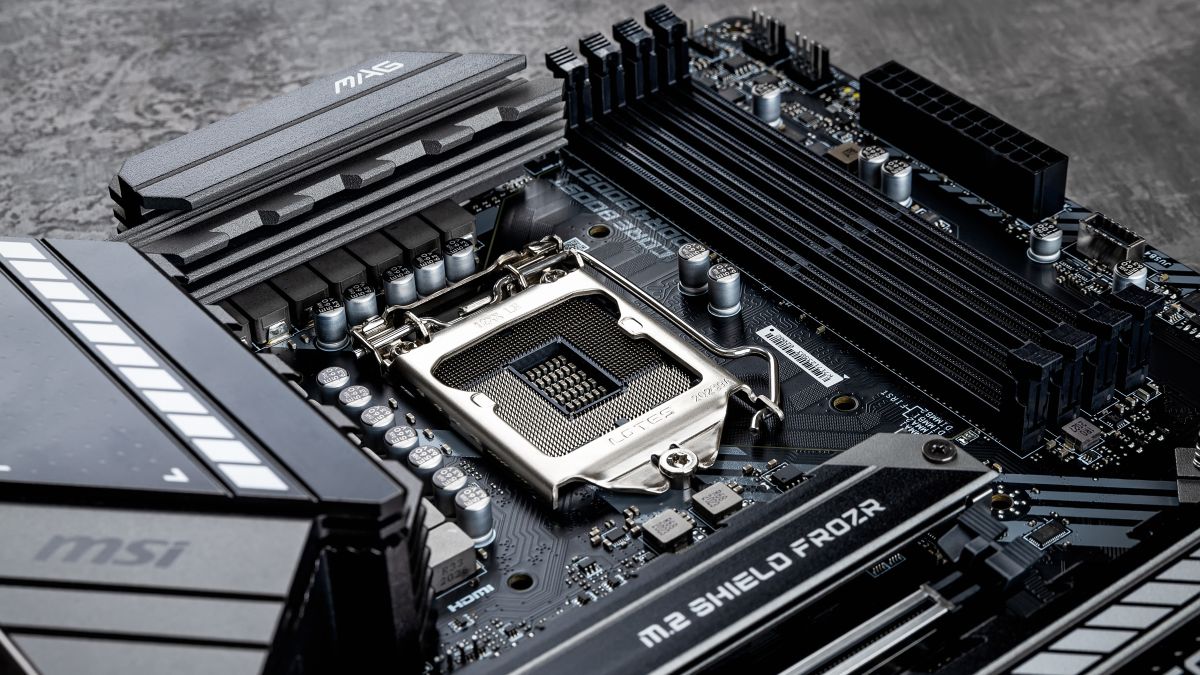
At its core, a motherboard is a printed circuit board (PCB) that provides the electrical connections between various hardware components in a computer. It serves as a platform upon which the CPU (Central Processing Unit), memory modules, storage drives, expansion cards, and other essential peripherals are installed and interconnected.
Different Types of Motherboards
- ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): This is the most common form factor for desktop motherboards. ATX boards typically offer multiple expansion slots and ample space for components, making them suitable for a wide range of computing needs.
- Micro-ATX: These motherboards are smaller than ATX boards but still offer a decent number of expansion slots. Micro-ATX boards are often used in compact desktops or budget-oriented builds where space is a consideration.
- Mini-ITX: Mini-ITX motherboards are even smaller than Micro-ATX boards, designed for ultra-compact systems such as home theater PCs (HTPCs) or small form factor gaming rigs. Despite their diminutive size, Mini-ITX boards still pack a punch with support for powerful CPUs and GPUs.
- E-ATX (Extended ATX): E-ATX motherboards are larger than standard ATX boards, offering more expansion slots and space for additional components. These boards are often favored by enthusiasts and professionals who require extensive customization options and high-performance capabilities.
- Server Motherboards: Designed for use in servers and enterprise environments, server motherboards prioritize reliability, scalability, and features such as multiple CPU sockets and support for ECC (Error-Correcting Code) memory.
Components on the Motherboard
- CPU Socket: The CPU socket is where the processor is installed. Different motherboards support different CPU socket types, so it’s essential to choose a motherboard that is compatible with your chosen CPU.
- Memory Slots: These slots accommodate RAM (Random Access Memory) modules, providing temporary storage for data that the CPU needs to access quickly.
- Expansion Slots: Expansion slots, such as PCI Express (PCIe) slots, allow you to install additional components like graphics cards, sound cards, network adapters, and storage controllers.
- Chipset: The chipset is a set of integrated circuits that manage communication between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other peripherals. It plays a crucial role in determining the motherboard’s features and capabilities.
- Storage Connectors: Motherboards feature various connectors for storage devices, including SATA (Serial ATA) ports for traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), as well as M.2 slots for high-speed NVMe SSDs.
- Power Connectors: Power connectors deliver electrical power to the motherboard and its components. These include the main ATX power connector, CPU power connector, and auxiliary power connectors for PCIe slots.
- Input/Output (I/O) Ports: These ports provide connectivity for peripherals such as USB devices, audio equipment, Ethernet cables, and display monitors.
Conclusion
The motherboard serves as the foundation upon which your computer is built, facilitating communication and coordination between all other hardware components. Understanding its different types and components can help you make informed decisions when building or upgrading your system. Whether you’re a casual user, a gaming enthusiast, or a professional seeking maximum performance, choosing the right motherboard is essential for unlocking the full potential of your computer.










Comments (0)